christophersi [S.](F)
Sergentomyia (Sintonius) christophersi (Sinton, 1927)
CARACTERES DIAGNOSTIQUES
Sintonius à fémurs inermes. Ce phlébotome se distingue de tous les autres Sintonius à fémurs inermes par son armature cibariale réduite : 2 à 3 dents principales, courtes et fortes chez le mâle, 4 à 5 dents fortes et aiguës chez la femelle.
DESCRIPTION
Phlebotomus christophersi Sinton,1927. Indian Journal of Medical Research, 15 : 33-40. [Mâle, femelle].
Statut actuel : Lewis, 1973.
TYPES
Lectotype femelle, Pakistan : Lahore, 20.VIII.1923 ; Paralectotype mâle (désignés par Lewis & Buttiker 1982) (Natural History Museum, Londres).
BIOLOGIE
Biotopes : terriers d’Acomys, en voisinage avec 3 autres espèces (Sergentomyia clydei, Phlebotomus bergeroti et Sergentomyia calcarata), abris sous roche d’une falaise de grès, habitations.
Fluctuations : inconnues.
Développement larvaire: inconnu.
Préférences trophiques: inconnues.
Importance médicale: rôle vecteur inconnu.
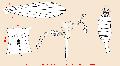
Sergentomyia (Sintonius) christophersi femelle
A. cibarium; B. pharynx; C. spermathèque; (lames # 2720, 2711, 2718, Guinée, IRD Coll.)
ABDOMEN
AILE
- AILE : Largeur de l'aile (mm) F : > 0,30 & <= 0,50
- AILE : Longueur de l'aile (mm) F : >1,75 & <= 2 ; >1,50 & <= 1,75
- AILE : Rapport longueur / largeur de l'aile F : > 4 & <= 5
GENITALIA
PATTE I
RÉPARTITION
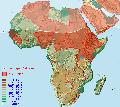
- RÉPARTITION : Espèces connues d'un pays donné : Arabie Saoudite (partie SW) ; Djibouti ; Érythrée ; Éthiopie ; Gambie ; Guinée ; Kenya ; Niger ; Nigeria ; Ouganda ; République Centrafricaine ; Sénégal ; Soudan ; Tchad ; Yémen
- RÉPARTITION : Espèces connues d'un pays et des pays limitrophes : Zanzibar (Tanzanie) ; Yémen ; Togo ; Tchad ; Tanzanie ; Soudan ; Somalie ; Sierra Leone ; Sénégal ; République Centrafricaine ; Pemba (Tanzanie) ; Ouganda ; Nigeria ; Niger ; Mauritanie ; Mali ; Liberia ; Kenya ; Guinée-Bissau ; Guinée ; Gambie ; Érythrée ; Djibouti ; Côte-d'Ivoire ; Congo Démocratique (ex-Zaïre) ; Congo ; Cameroun ; Burundi ; Burkina Faso ; Bénin ; Arabie Saoudite (partie SW)
SPERMATHÈQUE
- SPERMATHÈQUE : Aspect de la surface des conduits : strié
- SPERMATHÈQUE : Base des conduits individuels : dilaté ; non dilaté
- SPERMATHÈQUE : Conduits individuels : réunis à la base ; séparés
- SPERMATHÈQUE : Forme de la tête : en flamme de bougie
- SPERMATHÈQUE : Forme générale du corps : segmentée
- SPERMATHÈQUE : Tête de la spermathèque : sessile
TÊTE
- TÊTE : Alignement des dents du cibarium F : sur une ligne droite ou sinueuse
- TÊTE : Armature cibariale F : avec des dents bien marquées
- TÊTE : Aspect des dents cibariales F : les dents médianes comme les latérales
- TÊTE : Comparaison des segments antennaires AIII et AIV + AV : AIII < AIV + AV
- TÊTE : Denticules du cibarium F : 1 rangée de denticules
- TÊTE : Disposition des dents du cibarium F : ?
- TÊTE : Extrémité de l'hypopharynx : denticulée ; fortement ondulée ; faiblement ondulée ; lisse
- TÊTE : Extrémité des mandibules : dentée ; denticulée
- TÊTE : Forme de l'extrémité des dents cibariales : pointue
- TÊTE : Forme de la plage pigmentée du cibarium : en raquette de ping-pong
- TÊTE : Forme du pharynx postérieur : faiblement dilaté postérieurement
- TÊTE : Formule antennaire F : 2/III-XV
- TÊTE : Formule palpale F : 1-2-4-3-5 ; 1-(2-4)-3-5
- TÊTE : Longueur du segment antennaire AIII (µm) F : > 120 & <= 150
- TÊTE : Nombre de dents du cibarium F : 1 à 10
- TÊTE : Plage armée du pharynx F : peu étendue
- TÊTE : Plage pigmentée du cibarium F : étendue sur la partie médiane du cibarium
- TÊTE : Rapport segment antennaire AIII / Epipharynx F : <= 0.70
- TÊTE : Rapport segment antennaire AIV / ascoïde IV (c/b) F : >1 & <=2